hardness test using minor and major load|rockwell hardness m scale : manufacturer There are two types of Rockwell tests: • Regular Rockwell: the minor load is 10 kilograms of force (kgf) and the major load is 60, 100 or 150 . Divas del Fútbol, Bogotá, Colombia. 351,606 likes · 20,096 talking about this. Modelos que jugamos al fútbol 1️⃣3️⃣ Años Colombia ⚽️
{plog:ftitle_list}
27 de jan. de 2024 · Leggi su Sky Sport l'articolo Atalanta-Udinese 2-0, gol e highlights: Miranchuk-Scamacca, doppio assist De Ketelaere
The Rockwell test consists of measuring the additional depth to which a carbide ball or Brale® diamond penetrator is forced by a heavy (major) load beyond the depth of a previously applied light (minor) load (SET point). The minor load is applied first and a SET position is established .
Rockwell Hardness refers to a method of measuring the hardness of materials, particularly metals and alloys, by applying a minor load followed by a major load for a specific period of time and .First a Minor Load (one of a lesser force) is applied to a steel ball or sphero—conical diamond penetrator. Then, while the Minor Load is still being applied, a Major Load (one of greater force) is applied at a precisely .First, a preliminary test force (commonly referred to as preload or minor load) is applied to a sample using a diamond or ball indenter. This preload breaks through the surface to reduce the effects of surface finish. There are two types of Rockwell tests: • Regular Rockwell: the minor load is 10 kilograms of force (kgf) and the major load is 60, 100 or 150 .
Superficial Rockwell Testing. In this test method, the minor (preload) is always 3 kgf. The major load may be any of the following loads: 15kgf, 30 kgf, or 45 kgf. ASTM E18 contains a listing of all regular Rockwell scales and typical .
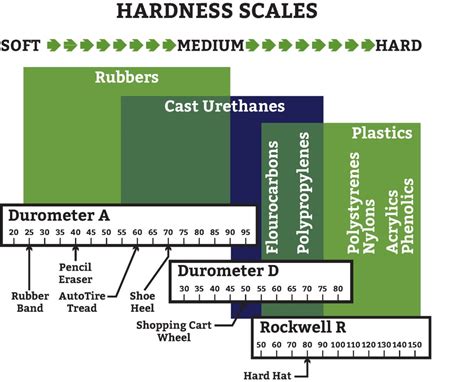
thermoplastic hardness chart
rockwell hardness tests pdf
The Rockwell hardness test is based on the difference of indenter depth from two load applications. An indenter is pressed into the material under an initial minor load to establish a . The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a . The Rockwell hardness test is based on the measurement of the depth to which an indenter is forced by a heavy (major) load beyond the depth resulting from a previously applied preliminary (minor) load.In this test, a standard minor load is applied to set a hardened steel ball or a diamond cone in the surface of the metal, followed by the application of a standard major load. The hardness is measured by depth of penetration.
Apply the major load: A major load of predetermined size and weight is then applied on the same spot using the same instrument for applying the minor load. Hold the major load in place for some time to make a deeper indentation. Taking the major load measurement: Using a dial or a measuring gauge, measure the depth of the indentation made by .Hardness Testing. G. Sundararajan, M. Roy, in Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, 2001 1 Macrohardness Testing 1.1 Rockwell Hardness Testing. In a Rockwell hardness test, initially a minor load of 10 N is applied and the zero datum position is established.The major load (60, 100, or 150 N) is then applied for a specific period (a few .The type of indenter and the test load determine the hardness scale(A, B, C, etc). A minor load of 10 kg is first applied, which causes an initial penetration and holds the indenter in place.Then, the dial is set to zero and the major load is .
To carry out Rockwell Hardness Testing, a sample is subjected to stress by a diamond cone or a hard steel ball. The test procedure involves applying a minor load to create an indentation in the material to measure the depth of penetration. Subsequently, a major load is applied, and the penetration depth is measured again.Hardness Methods: The Rockwell hardness test measures the depth of penetra-tion of an indenter into a material under a known load. It provides a hardness value based on the depth of penetration. Rockwell Hardness The Brinell hardness test involves indenting a material with a hard sphere under a specific load. Two diameters (x and y
rockwell hardness scale chart
the minor load prior to the major load being deployed and the depth associated with the minor load after the major load is withdrawn. There are two general classes of Rockwell test: Rockwell and superficial Rockwell. In Rockwell testing, the minor load is 10 kgf and the major load is 60, 100 or 150 kgf. In superficial Rockwellthe minor load prior to the major load being deployed and the depth associated with the minor load after the major load is withdrawn. There are two general classes of Rockwell test: Rockwell and superficial Rockwell. In Rockwell testing, the minor load is 10 kgf and the major load is 60, 100 or 150 kgf. In superficial Rockwell
There are two types of Rockwell test (Table 23.1): Rockwell: the minor load is 10 kgf, the major load is 60, 100, or 150 kgf. Superficial Rockwell: the minor load is 3 kgf and major loads are 15, 30, or 45 kgf. Table 23.1: Some common scales in Rockwell and Superficial Rockwell testing Understanding Vickers’s Hardness Test. I use Vickers’ Hardness Test which can be used across different materials thereby enabling me identify material’s level of brittleness.This involves pressing the diamond pyramid indenter with square base and an angle of 136 degrees together with the opposing faces into the surface of a sample.In this test, a standard minor load is applied to set a hardened steel ball or a diamond cone in the surface of the metal, followed by the application of a standard major load. The hardness is measured by depth of penetration. Rockwell superficial hardness tests are made using light minor and major loads and a more sensitive system for .Here’s how it works: When conducting a Rockwell hardness test, an indenter is used to press against your material with two loads; a minor load first, then followed by a major load. The difference in depth between these two loads provides the Rockwell hardness number (RHN). Imagine using different amounts of pressure on a scale to see how far .
is the abo test hard
specified constant load into the surface of material and measuring the length, width, or depth of the indentation. Each hardness test method, or scale, is defined with a particular type of indenter, a specified minor load, and a specified major load. The measured indentation size is then converted to a hardness number specific to the scale adopted.D = The difference in heights between the indentation caused by major load and minor load. This difference in height helps to determine the Rockwell Hardness Number. . Also, as the hardness of the test samples increases, it becomes continuously challenging to use Rockwell hardness testing in distinguishing various materials. As a result . Hardness Testing Loads. The hardness testing load is the load (“force”) that is applied to the indenter when pressing into the material being tested. The depth or size of the deformation made by the indenter will depend directly on the load that was used to press it in. This load is applied by a machine, a hardness testing device. When Rockwell hardness testing, a minor load of 10kg is applied to the indenter used on the material being tested. The purpose of the minor load is to penetrate the material’s surface and establish a set position. .
The Rockwell hardness test is based on the measurement of the depth to which an indenter is forced by a heavy (major) load beyond the depth resulting from a previously applied preliminary (minor) load. . Superficial Rockwell: the .In the Rockwell hardness test, a differential-depth method, the residual depth of the indent made by the indenter, is measured.In contrast, the size of the indentation is measured in the Brinell, Vickers and Knoop optical test . Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following statements is true about microhardness testing?, Which portable hardness testing method measures the rebound of a ball hammer that is bounced off of the material with a spring mechanism?, Which hardness testing method determines a hardness value after delivering .
In Rockwell testing, the minor load is 10 kgf, and the major load is 60, 100 or 150 kgf. In superficial Rockwell testing, the minor load is 3 kgf, and major loads are 15, 30 or 45 kgf. In both tests, the indenter may be either a diamond cone or steel ball, depending principally on the characteristics of the material being tested.A minor load is applied and a zero reference position is established. The major load is applied for a specified time period (10 to 15 seconds) beyond zero. The major load is released, leaving the minor load applied. Follow the process to determine .
Vickers hardness test. Load 0.5 kgf1. Final preparation on surface MD-Largo with diamond suspension DiaPro Allegro/Largo 9 (9 µm). . regular Rockwell where the minor load is 10 kgf, the major load is 60, 100 or 150 kgf; and Superficial Rockwell, used for thinner specimens where the minor load is 3 kgf and major loads are 15, 30 or 45 The net increase in dent dimension (between the application of minor and major load) is considered for calculating the hardness value. . d – depth of permanent indentation compared to minor load, mm. Vickers Hardness Test. Vickers Hardness Test The third way for measuring material hardness is using the Vickers test. This is especially . 3.Major Load Application:The major load is applied,causing the indenter to penetrate further into the material's surface. 4.Load Removal:The major load is removed,while the minor load still acts on the indenter. 5.Depth Measurement:The depth of penetration under the minor load is measured using a depth-measuring system.The Rockwell hardness number is calculated from the depth of permanent deformation of the indenter into the sample, i.e. the difference in indenter position before and after application of the major load. The minor and major loads can be applied using dead weights or springs. The indenter position is measured using an analog dial indicator or .

Learn all you need to know about Rockwell hardness testing – including test definitions, test calculations and insight into Rockwell hardness testing machines and HRC hardness testers – with knowledge and expertise from Struers, the world’s leading materialographic and metallographic experts. . 100 kgf major load; HR30N (Superficial . Allow the minor load to stabilize, ensuring that the indenter is correctly positioned on the material. Apply major load. Once the minor load is stable, apply the major load. The major load can range from 60 to 150 kgf, depending on the specific Rockwell scale being used. This load creates a deeper indentation in the material. Hold the loadWhich hardness testing method uses a 15N Scale? and more. . Which hardness testing method employs either a ball or a diamond penetrator, and a load o f 15kg, 30kg, or 45kg? Rockwell superficial. 13. In which hardness testing method is the hardness value based on the diameter of an indenture?
rockwell hardness m scale
Find Versus Png stock images in HD and millions of other royalty-free stock photos, 3D objects, illustrations and vectors in the Shutterstock collection. Thousands of new, high-quality pictures added every day.
hardness test using minor and major load|rockwell hardness m scale